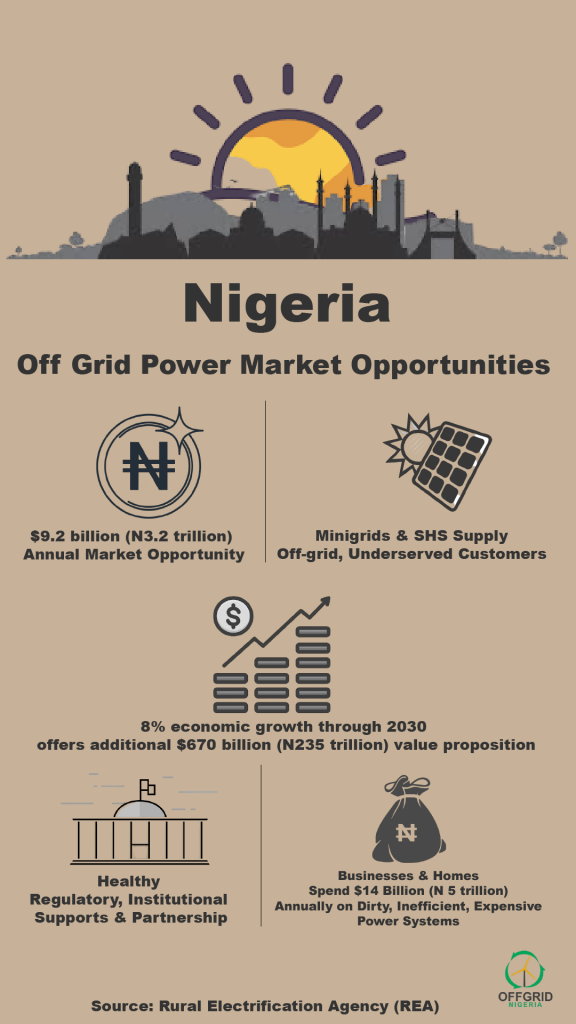
To meet the 30,000 megawatts (MW) clean electricity target it set in the Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) submitted in the Paris Climate Change pact, Nigeria’s solar photovoltaic (PV) market would need about 200 million batteries over the next 20 years.
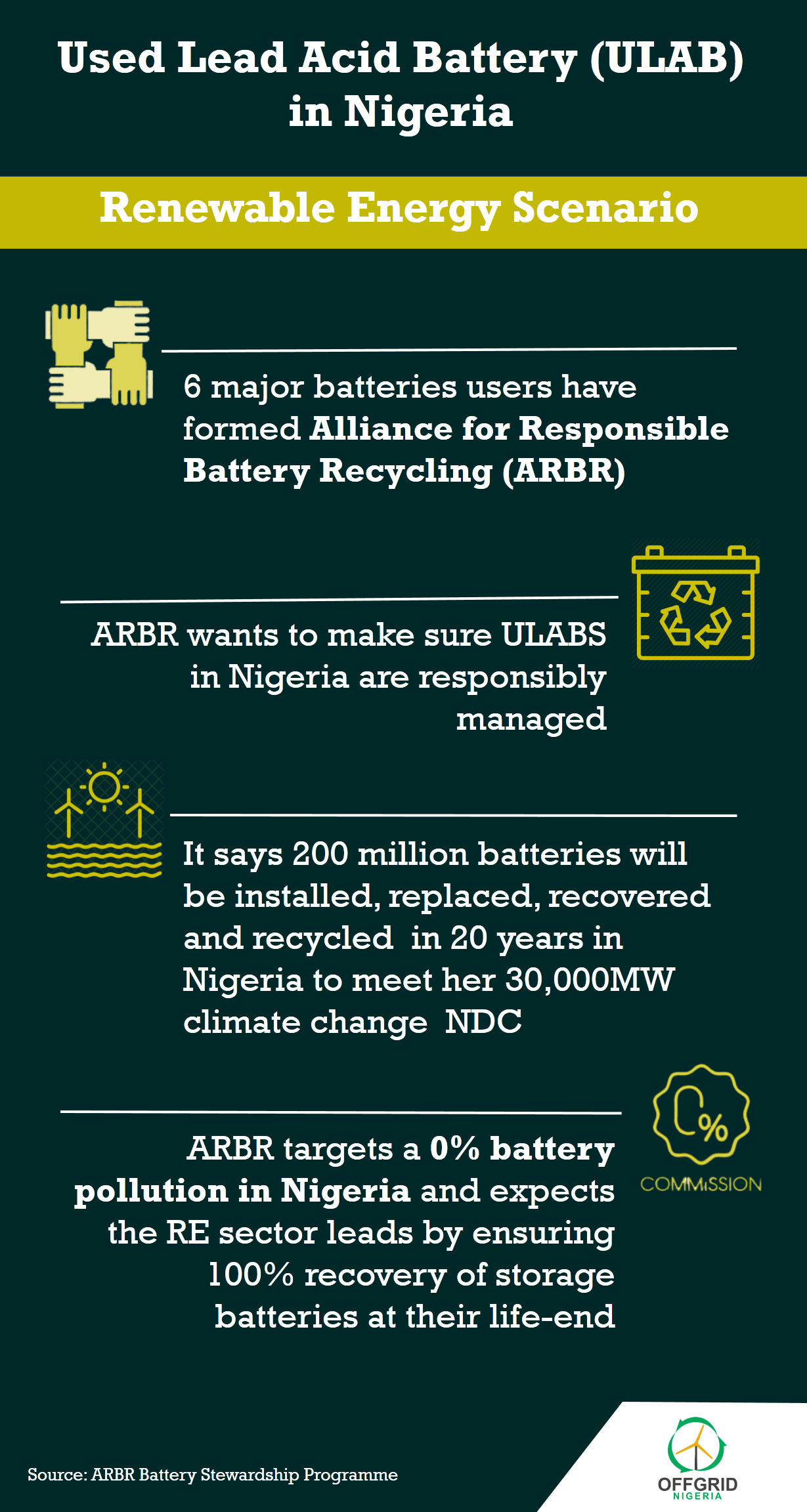
A new report written by the Alliance for Responsible Battery Recycling (ARBR) on responsible storage battery usage and management in the country’s power sector disclosed this.
The report titled, ‘Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) for the Nigerian Battery Sector: A Battery Stewardship Programme for the Solar Mini Grid and Renewable Energy Sector’, was recently presented workshop on used lead acid battery (ULAB) organised by renewable energy firm, Cleantech Hub.
What the report said
It explained that for Nigeria to generate up to 30,000MW of clean electricity from solar PVs, it will initially have to install 40 million batteries in the first few years. This number is expected to rise over 20 years to 200 million as they outlive their four-year lifespan.
According to it, as a fast-developing economy with a growing population, higher demand for solar energy and automobiles has led to large quantities of batteries imported into the Nigerian market with little or no responsibility for their end-of-life stages.
The report said that the lack of responsibility in batteries’ end-of-life management has led to unintended consequences for the environment and human health caused by informal dirty recycling.
“Used batteries from the fast-growing solar industry are projected to surpass the automobile sector in few years. For every 6kilowatt (KW) solar PV installation about eight (200 Amp, 48 V) batteries are needed.
“For metropolitan residences about 24 batteries are needed, for small apartments or rural households about two to four batteries depending on the energy consumption needs,” said the report.
It further stated: “Nigeria’s solar PV target is projected at 30,000MW according to the Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), this would require a huge amount of batteries.
“To generate 30,000MW of electricity, about 40 million batteries will be needed initially. With an average lifespan of 4years for a Led Acid Battery, compared to 20 years lifespan of the PV panels, 200 million batteries will have to be installed, replaced, recovered and recycled within this period.”
Large scale power projects mean more batteries
Further, the reported noted that while the Ministry of Power was executing large solar energy projects, mini grid projects and equally signed Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) to generate 2000MW by 2020, it would also need more batteries for energy storage.
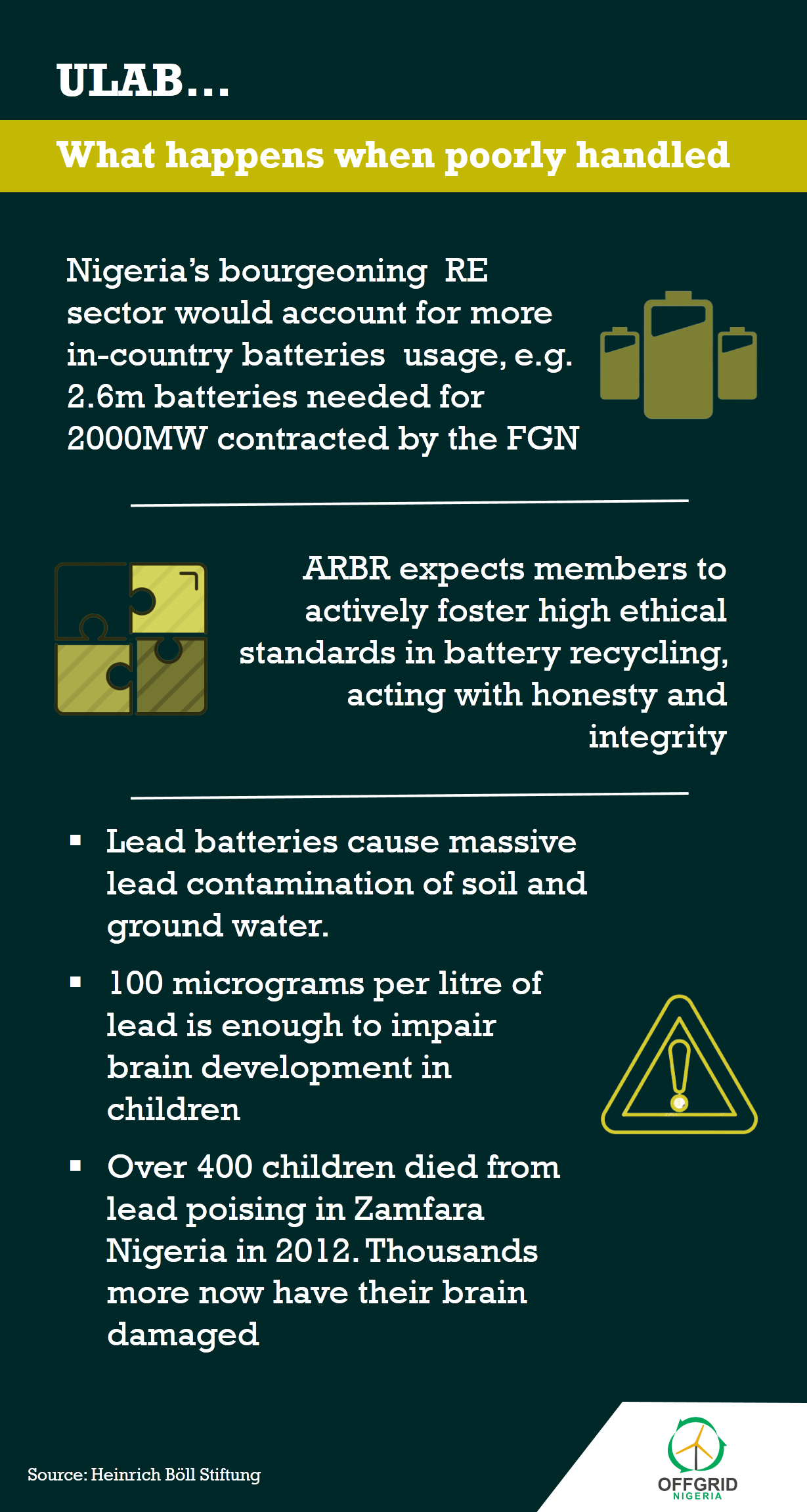
“This means at least 2.6 million batteries, or 52,000 tons of batteries will be installed for solar projects in the next one or two years. When added to batteries from small home systems, solar streetlight projects, the challenge of managing used batteries becomes clearer,” it explained.
To ensure that the batteries end-of-life processes are managed well, the report which was prepared by the Alliance for Responsible Battery Recycling (ARBR), said: “In order to make significant impact, we must set a zero-pollution policy in the battery industry.
“The renewable energy sector acclaimed as green and clean energy must take the lead in implementing this battery recycling programme for the sector. The target is to ensure that all energy storage batteries installed with Solar PV panels are 100 per cent recovered at their end-of- life and recycled through licensed and clean processes to prevent hazardous pollution from illegal and dirty battery recycling activities.”